 The emergence of a new generation of smart industrial connectors is playing a key role in enhancing the flexibility and efficiency of industrial processes. By integrating intelligent active device technology directly at the field connectivity level, connectors such as the Han® ID Module enable manufacturers to improve the operational performance of machines using a modular “plug & play” control architecture, supporting the Industry 4.0 smart factory philosophy for ongoing production process improvements.
The emergence of a new generation of smart industrial connectors is playing a key role in enhancing the flexibility and efficiency of industrial processes. By integrating intelligent active device technology directly at the field connectivity level, connectors such as the Han® ID Module enable manufacturers to improve the operational performance of machines using a modular “plug & play” control architecture, supporting the Industry 4.0 smart factory philosophy for ongoing production process improvements.
Such connectors are able to separately identify each machine module and store such information within the main automation system via a direct interface to the I2C or CAN network control bus. Each machine module can then be instantly recognised as it is fitted or replaced within the system, saving machine set-up time and limiting operator error by ensuring that the correct module is applied according to the operational requirements.
Besides the identification of components and machine elements, these smart connectors are also increasingly being deployed in predictive maintenance operations.
These applications are greatly facilitated by communica-tions via inexpensive bidirectional systems like the I2C bus, as well as standardised bus systems such as the CAN Bus and Ethernet profiles like Profinet. A new development in this area, in addition to the already established ID module described above, is the smart CAN ID module.
Implementation as a Han Modular® module ensures that identification is flexibly integrated into space-saving interfaces which comprehensively supply machines with power, data and signals.
The progress made by transferring identification functionality to the connector can best be illustrated by differentiating between processing machinery intended for mobile use and machinery with isochronous drives.
Case 1: ID module in mobile processing machinery with interchangeable elements
On machinery with pluggable drives, auxiliary equipment and other machine units, ID modules help to determine if the units are in the right slot. They consequently avoid erroneous configuration. Information such as the year of manufacturing, the last revision status and other parameters of the machine unit can also be stored and used for predictive maintenance on the application. In this case, the ID module has a double function as identification tool and data memory.
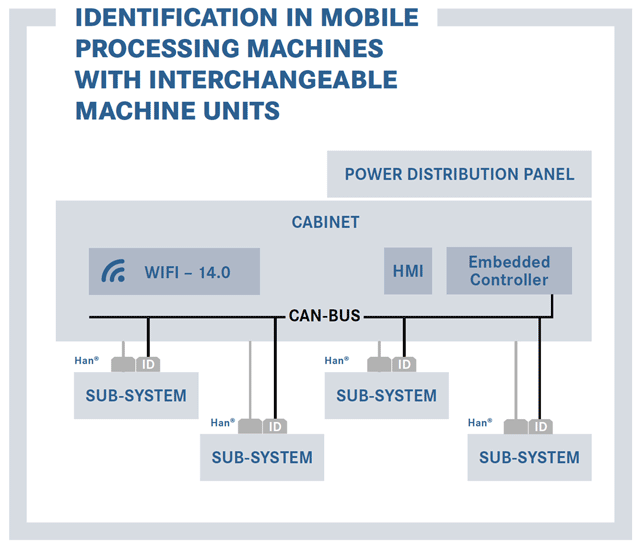 The customer benefits derive from the fact that erroneous insertion of a machine unit is prevented. Moreover, there is also memory space for additional subordinate, area-relevant information. The ID module paves the way for the customisation of the machine unit.
The customer benefits derive from the fact that erroneous insertion of a machine unit is prevented. Moreover, there is also memory space for additional subordinate, area-relevant information. The ID module paves the way for the customisation of the machine unit.
In addition to local machine control, industrial Wi-Fi modules provide easy connection with the Industry 4.0 manufacturing environment.
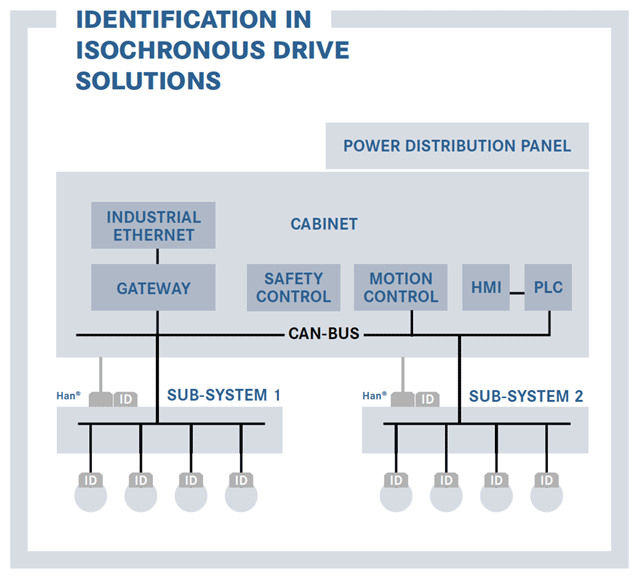
Case 2: ID module in pluggable isochronous drives
Both conventional machinery and special-purpose machinery contain machine components characterised by movement processes made up of individual synchronously executing movements.
 In conventional machinery, this synchronicity is often achieved by using line shafts, which employ cams and other power couplings to initiate all movements according to a defined process scheme.
In conventional machinery, this synchronicity is often achieved by using line shafts, which employ cams and other power couplings to initiate all movements according to a defined process scheme.
However, machines with high speeds and accelerated axes are controlled using special sensors, drives and motion controllers.
The CAN Bus, which functions in real time and is organised according to the “publisher-subscriber” principle, is ideally suited for the synchronisation of subscribers. The CAN ID Module also enables the current configuration of the drives to be tested and the parameters that are determined to be transmitted to all other drives and the controller.
The machine may only start up if the drive is correctly configured. Start-up is blocked if any state exists other than the one desired.
The benefit for the customer is the potential for time savings, for example during servicing: drive data is available in the module at the periphery, meaning that the revision status can be quickly queried.
Individual machine elements can be exchanged and repaired faster, since work on a subsystem does not entail starting the entire machine. This saves time and energy.
Consequently, the CAN ID Module offers advantages for both types of machinery. On the one hand, it helps implement identification functionality in combination with memory storage capabilities in the device periphery, while on the other, it logically complements existing complex systems and helps save time and money on servicing.
For Industry 4.0 applications, integration takes place via network-enabled devices or, in future, directly via an Ethernet interface. This in turn implements end-to-end networking of the data.
www.HARTING.co.uk
salesUK@HARTING.co.uk
Tel: 01604 827500

